The Events Listed Below Generally Take Place During Meiosis.
Important events of meiosis are. In each circle on the diagram write the letter of the job listed below that the body part does.
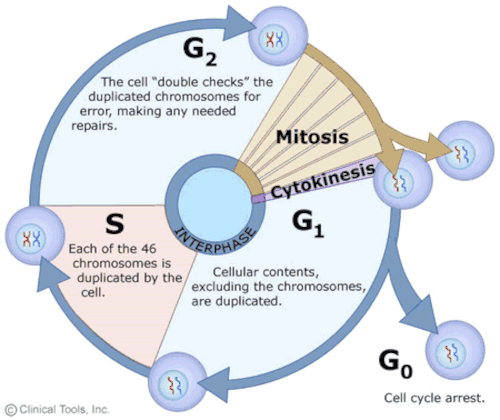
The Cell Cycle Mitosis And Meiosis For Schools And Colleges Virtual Genetics Education Centre University Of Leicester
The chromatin condenses into chromosomes.

. Condensation of chromosomes begins. Most of the skeleton of a human embryo is composed of connective tissue known as. Oviduct ovary uterus egg vagina.
Condensation of chromosomes begins. During the interphases of meiosis each chromosome is duplicated. The embryo is protected from shock by a substance located at.
Condensation of chromosomes begins. 1 Events in meiosis result in variation. During _____ the chromotids generally decondense somewhat the nuclear envelope may reorganize and cytokinesis may take place.
The nuclear membrane and nuclei break up while the spindle network appears. 3 Differentiated cells have different genes. In prophase II of meiosis the following events occur.
The chiasmata are thought to be the points where two non-sister chromatids. Receives sperm during mating. The process by which homologous become joined to one another during meiosis.
7 A change in the base subunit sequence during DNA replication can result in 1 variation within an organism. Crossing over Genetic recombination. First is the condensation of chromatin into chromosomes the second aspect is the physical contact between homologous chromosomes and the third aspect is the transmission of genetic information between synapsed chromosomes.
Crossing over between homologous chromosomes during prophase I. These chromosome copies are. Try one of the other activities listed below the flashcards like.
Chromosomal crossover or crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes that results in recombinant chromosomes during sexual reproduction. As with mitosis DNA replication occurs prior to meiosis during the S-phase of the cell cycle. A I II III IV B II I III IV C III I II IV D III IV II I E IV II III I.
Which of the following is. Cell formed in the ovary. Centrosomes migrate to either poles.
Independent assortment of homologous chromosomes during meiosis I and of nonidentical sister chromatids during meiosis II. The G 1 phase the first gap phase is focused on cell growth. In this phase the cell undergoes the final preparations for meiosis.
The chromosomes begin migrating to the metaphase II plate at the cells equator. The events listed below generally take place during meiosis. Finally the G 2 phase also called the second gap phase is the third and final phase of interphase.
Results in producing genetically identical cells d. Stage of meiosis telophase I _____ is an interphase-like stage but not a true interphase - there is no S phase and therfore no DNA replication. Finally in the G 2 phase the second gap phase the cell.
Muscular organ where fertilized egg develops. 1 Prophase 1. Finally in the G 2 phase the second gap phase the cell undergoes the final preparations for meiosis.
During the S phasethe second phase of interphasethe cell copies or replicates the DNA of the chromosomes. Spindle fibres are reformed. On the contrary the chromosomes in metaphase I were in homologous pairs.
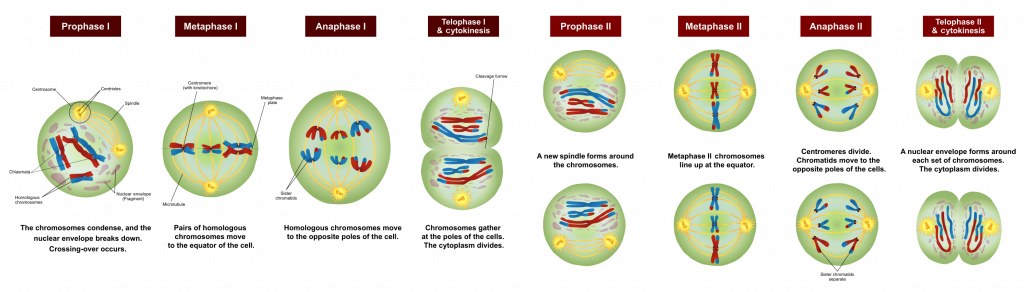
Meiosis is a series of events that arrange and separate chromosomes and chromatids into daughter cells. Prophase 1 is the longest phase of meiosis where three primary aspects are taking place. Reduces the number of chromosomes c.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of these events. 4 Half the genetic information in offspring comes from each parent. Separation of homologous chromosomes begins.
Separation of homologous chromosomes begins. Involves two divisions b. Occurs in the gonads.
During DNA duplication in the S phase each chromosome is replicated to produce two identical copies. The S phase is the second phase of interphase during which the DNA of the chromosomes is replicated. 1 Two successive cell division without DNA replication 2 Pairing of homologous chromosomes during prophase I followed by formation of chaismata and crossing over that lead to genetic variation 3 Separation of homologous chromosomes in anaphase I of meiosis I.
Meiosis II Prophase II. Produces haploid cells e. The events listed below generally take place during meiosisI.
Chromosomes do not replicate any further in this phase of meiosis. Meiosis is preceded by an interphase consisting of G 1 S and G 2 phases which are nearly identical to the phases preceding mitosis. The three sources of genetic variability in a sexually reproducing organism are.
The development of an embryo is represented in the diagram below. Four of the five answers listed below are the characteristics of meiosis. A The events listed below generally take place during meiosis.
Synapsis is the pairing of two homologous chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. A place where the egg is formed. A I II III IV II I III IV III I II IV B C.
The events listed below generally take place during meiosis. 2 Gene expression can be influenced by the environment. At the end of prophase II of meiosis the cell enters into metaphase II.
Reshuffling of the genes on chromosome that occurs during meiosis as a result of breakage and reunion of segments of homologous chromosomes Synapsis. Crossing over is the most important genetic phenomenon of meiosis which causes variation in genetic characters in offspring. The process of crossing over starts crossing over.
Label the diagram below using these words. A small fragment of chromosome exchange between two non-sister chromatids of bivalent by breakage and rejoining. The events listed below generally take place during meiosis.
Separation of homologous chromosomes begins. During DNA duplication in the S phase each chromosome is replicated to produce two identical copiessister chromatids that are held together at the centromere by cohesin proteins which hold the chromatids together until anaphase II. Select the exception a.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of these events. Condensation of chromosomes begins. Base your answer on the diagram below which represents a necessary part of human reproduction.
Separation of homologous chromosomes begins. The chromosomes align along the equatorial plate. Random fertilization of an ovum by a sperm.

Meiosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

4 1 Meiosis Biology Libretexts

Topic 1 3 How Do Living Things Sexually Reproduce Ppt Download

Difference Between Dinner And Supper With Table Descriptive Word Cloud Emotions
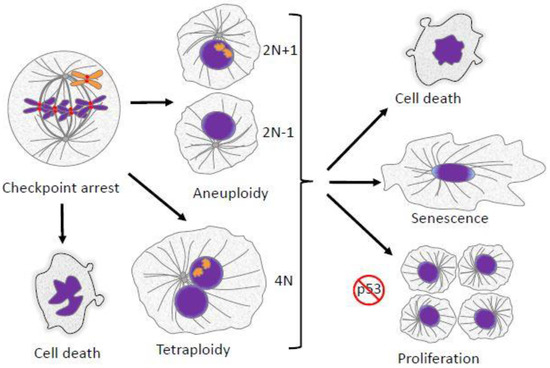
Biology Free Full Text The Consequences Of Chromosome Segregation Errors In Mitosis And Meiosis Html

Stages Of Meiosis And Sexual Reproduction Learn Science At Scitable
7 3 Errors In Meiosis Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition

Meiosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Coordinating The Events Of The Meiotic Prophase Trends In Cell Biology
Kinetochore Microtubule Attachment Biology Cell Biology Ap Biology

Diffusion And Distal Linkages Govern Interchromosomal Dynamics During Meiotic Prophase Pnas

Cell Cycle Definition Phases Regulation And Checkpoints Cell Cycle Cell Regulators

Mitosis Vs Meiosis Key Differences Chart And Venn Diagram Technology Networks

Meiosis In Humans The Embryo Project Encyclopedia

Pin On Ultimate Homeschool Board

Topic 1 3 How Do Living Things Sexually Reproduce Ppt Download

Comments
Post a Comment